Bridging the Digital Divide: the Promising Impact of TinyML for Developing Countries
Bridging the Digital Divide: the Promising Impact of TinyML for Developing Countries
Abstract
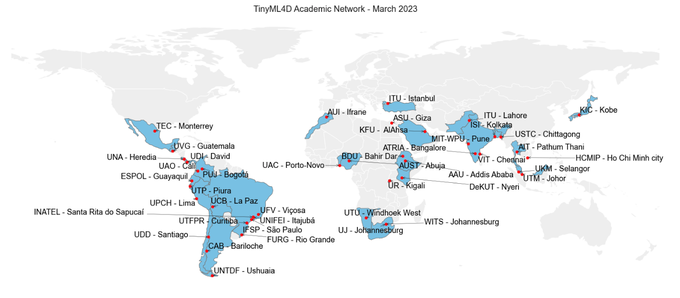
The rise of TinyML has opened up new opportunities for the development of smart, low-power devices in resource-constrained environments. This technology has particular relevance for developing countries, where access to energy and computing resources is often limited. In light of this, a network of 40 universities has been established over the past two years with the goal of promoting the use of TinyML in developing regions. The members of this network have taught courses at their home institutions and have completed their first research projects covering topics ranging from the diagnosis of respiratory diseases in Rwanda to assistive technology development in Brazil, bee population monitoring in Kenya and estimating the lifespan of the date palm fruit in Saudi Arabia. These initial projects demonstrate the potential for TinyML to make a real impact on the Sustainable Development Goals. They hold great promise for a new generation of devices that could help to bridge the digital divide and bring the benefits of technology to those who need it most. Lastly, we suggest three policy recommendations to increase the future impact: first, training and research activities in STI should focus on regional networks; second, the ethics of artificial intelligence must be covered in all activities; and third, we need to support local champions better.